Fiscal Policy
In 2010, Germany cut 14 million euros in taxes as agreed by the outgoing government coalition of Christian Democrats and Social Democrats. In 2011, they are aiming to cut 24 million euros in income taxes benefiting in particular low- and middle-income earners as well as families. There are still many details to go into this plan, but regardless Germany's goal is to cut income taxes tremendously. This represents an expansionary fiscal policy as Germany is decreasing taxes.
http://www.roubini.com/critical-issues/62084?parent_briefing=49792
http://www.roubini.com/critical-issues/62084?parent_briefing=49792
Impacts
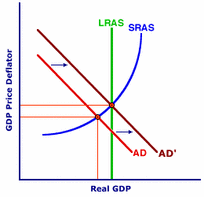
With expansionary policy comes the goal to close a recessionary gap, decrease unemployment, and stimulate the economy. Reducing taxes creates an opportunity for the economy to adjust itself while government spending can create new jobs. With more jobs and less taxation on income, this will help contribute towards closing the recessionary gap and stabilizing the economy.
Monetary Policy
Germany does not have its own money so they can not use their own monetary policy. Germany has to abide by what the ECB (European Central Bank) says. The ECB is expected to raise interest rates 1.5% by the end of this year. This is Alan Brown at Schroders said, "So we think what the ECB is doing here is sending a signal it is not going to let inflation expectations rise, although we are actually expecting headline inflation to begin to fall back, providing a justification for the ECB to slow its hand." He also said that the ECB has always been "hawkish" when dealing with inflation rates and what they spell out for the future.
http://www.investmentweek.co.uk/investment-week/news/2068955/brown-ecb-hike-rates
http://www.investmentweek.co.uk/investment-week/news/2068955/brown-ecb-hike-rates
Impacts
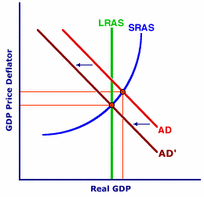
This rising of interest rates will not effect only Germany, but all the rest of the countries that are involved in the ECB. This can result in unstable prices, and alter many costs of living making it harder for citizens to get approved for loans on many things. It increases the cost of borrowing, increases mortgage income payments, increases incentive to save rather than to spend, rising interest rates affect both consumers and firms, and government debt interest payments increase. Although, the article made it seem like 1.5% was not a lot for the ECB, and made it sound almost positive in a way.
Sources
http://www.amosweb.com/cgi-bin/awb_nav.pl?s=wpd&c=dsp&k=contractionary+fiscal+policy
http://economics.about.com/cs/money/a/policy_2.htm
http://www.roubini.com/critical-issues/62084?parent_briefing=49792
http://agmetalminer.com/2010/06/29/soros-highly-critical-of-german-monetary-policy/
http://www.amosweb.com/cgi-bin/awb_nav.pl?s=wpd&c=dsp&k=contractionary+fiscal+policyhttp://www.investmentweek.co.uk/investment-week/news/2068955/brown-ecb-hike-rates
http://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/monetary-policy/effect-raising-interest-rates.html
http://economics.about.com/cs/money/a/policy_2.htm
http://www.roubini.com/critical-issues/62084?parent_briefing=49792
http://agmetalminer.com/2010/06/29/soros-highly-critical-of-german-monetary-policy/
http://www.amosweb.com/cgi-bin/awb_nav.pl?s=wpd&c=dsp&k=contractionary+fiscal+policyhttp://www.investmentweek.co.uk/investment-week/news/2068955/brown-ecb-hike-rates
http://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/monetary-policy/effect-raising-interest-rates.html
